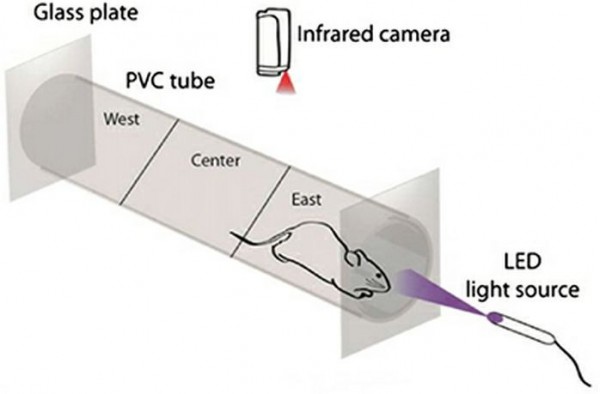
Eyesight restoration has deservedly been the subject of much research over the years. Recently, researchers have discovered a chemical that temporarily restores vision to blind mice. Now, the team is working on an improved compound to restore vision in people.
Earlier, we’ve seen efforts to restore human eye-vision through stem cell injections. And now, a team of University of California, Berkeley scientists, in collaboration with researchers at the University of Munich and University of Washington, has discovered a photochemical that can restore vision in blind mice for a few hours.
The name of that chemical is AAQ (acrylamide-azobenzene-quaternary ammonium). AAQ is a photochemical molecule ( in other words photoswitch) that binds to protein ion channels on the surface of retinal cells. In short, this chemical focuses on the damaged sensitive cells (neurons) of the eye. First, the AAQ is injected into the eyes of blind mice. When switched on by light, AAQ alters the flow of ions through the protein ion channels and activates the neurons. As soon as the neurons are being activated, the mice starts to see again. The restored vision lasts for few hours.
Just a small amount of AAQ can generate this effect for a few hours at a time. Scientists are trying to find something better that could let blind mice see for days rather than hours. After this breakthrough discovery, researchers are also working on an improved compound that may someday allow people with degenerative blindness to see again.
Source : University Of California, Neuron Journal
Thanks To : PopSci
[ttjad keyword=”electronic”]