Every now and then, scientists are creating new materials. Lately, scientists from the University of Southern Denmark have developed a new material that can suck all the oxygen out of a room.
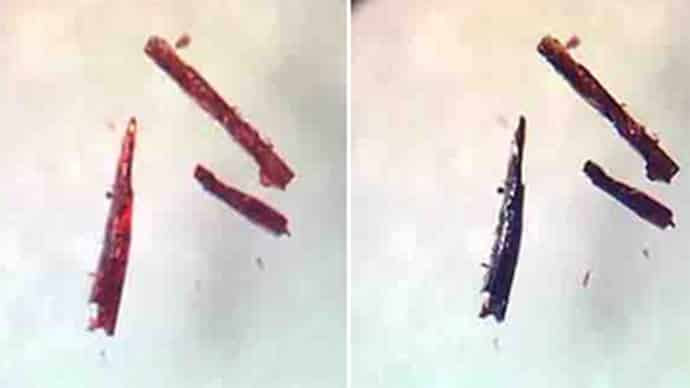
The scientists have developed a new form of crystalline cobalt salt that acts like a super-effective oxygen sponge. Once it sucks up oxygen, it will hold on to it indefinitely until it is gently heated or exposed to low oxygen pressure, at which point it will quietly release its oxygen hoard back out into the atmosphere. About 10 liters of it would be needed to suck all of the oxygen out of an average-sized room.
Christine McKenzie, lead scientist and nano-bioscience professor said in a press release, “The material can absorb and release oxygen many times without losing the ability. It is like dipping a sponge in water, squeezing the water out of it and repeating the process over and over again. When the substance is saturated with oxygen, it can be compared to an oxygen tank, containing pure oxygen under pressure. The difference is that this material can hold three times as much oxygen.”
The material works by forming a chemical bond with individual oxygen molecules, sort of how oxygen molecules bind with a blood protein called haemoglobin when we breathe, so the oxygen can be distributed around our bodies. Just like haemoglobin, this new material can both sense and contain oxygen, which means it can be used to bind, store and transport it for a range of different applications, from medical equipment to new scuba diving technology. Note that, the key to the material’s success in trapping and holding such a large amount of oxygen molecules is its lattice crystalline structure.
The team hopes to use this new material to replace hefty oxygen tanks used by scuba divers and mountain climbers. besides, this new material could play a vital role in on medical treatments. Scientists’ research has been published in the journal Chemical Science.
Source: University of Southern Denmark
Thanks To: Science Alert
[ttjad keyword=”t-mobile-contract-phone”]




dellmont voip [url=https://otvetnow.ru]https://otvetnow.ru[/url] fixing cracks in drywall