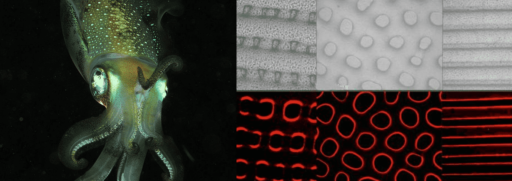
We caught this interesting development on PHYS.ORG today. A group of scientists at the Georgia Institute of Technology has found a new way to increase boiling efficiency by 17% using acoustic techniques. They have used acoustic field to enhance heat transfer and boil the fluid faster. The acoustic field increases the heat transfer by removing the vapor bubbles from the heated surface and eliminates the formation of insulating vapor layer on the heated surface in this way. This, in turn, heats the fluid more efficiently and makes it boil faster.
The breakthrough has been achieved by utilizing the characteristics of acoustic field. The acoustic field induces capillary waves (a wave traveling along the phase boundary of a fluid, whose dynamics are dominated by the effects of surface tension) on the bubble. This capillary waves cause the fluids contact line to contract and detach the bubble from the surface. When vapor bubbles are efficiently removed from the heated surface and suppressing the formation of an insulating vapor film, the heat transfer increases and leads the fluid boil faster.
Three acoustic experiments were done to explore the mechanisms associated with the interactions among acoustic fields, fluid and heated surface – one with an air bubble on the underside of a horizontal surface, another with a single vapor bubble on the top side of a horizontal heated surface, and the last with pool boiling from a horizontal heated surface. These experiments let the researchers measure the dominant forces in acoustically forced motions.
These discovery could lead to efficient use of energy in different industries as well as households, and reduce our carbon footprint. What do you think?
Source : American Institute of Physics (AIP)
[ttjad keyword=”sprint-contract-phone”]